Carotid Angioplasty
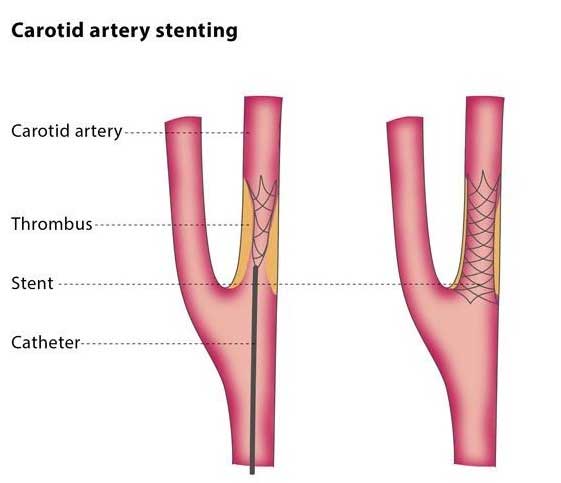
Sometimes the blood flow to the brain can be reduced due to build-up of plaque in the carotid arteries, the blood vessels that supply blood to the brain, which can lead to serious complications such as brain strokes.
Carotid angioplasty is a pinhole minimally-invasive non-surgical procedure that can help to effectively reopen these arteries and normalize the blood flow to brain.
This procedure is usually performed under light sedation or local anaesthesia by an expert Interventional Radiologist, who navigates to the blockage site under real-time imaging. Once the appropriate position is confirmed, the balloon is inflated which presses against the inside wall of the artery, thereby opening it and restoring the normal blood flow to the brain.
Many times stents (small flexible metal tube) are also placed in the artery to support the artery wall and keep it open.
The recovery period for this procedure is very short and the patient is usually discharged on the next day of the procedure after a period of observation.
Peripheral Angioplasty
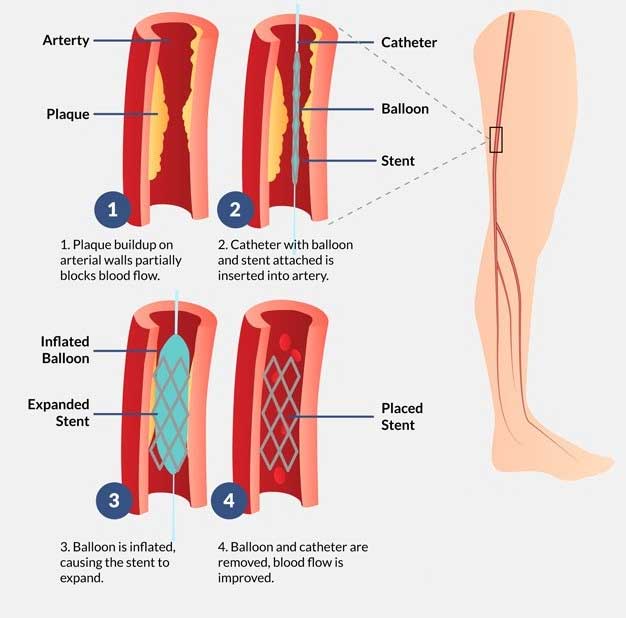
In a person with Peripheral Artery Disease, a common circulatory problem, plaques build up in the arteries (blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to organs) that obstruct blood flow to the extremities (peripheries), usually the legs. The most common symptom of PAD is leg pain (intermittent claudication) while walking or exercising.
One of the most successful and minimally invasive treatments for PAD is Angioplasty. This highly specialized procedure is performed by an Expert Interventional Radiologist and is usually performed under local/regional anesthesia. Utilizing high resolution fluoroscopic (X-ray) imaging monitoring, a catheter, which holds a small balloon, is inserted through a pinhole-sized incision (cut) into the skin and guided through to the peripheral artery that is to be treated. After verifying proper catheter placement, the balloon is inflated that breaks up the plaque and opens the blocked blood vessel restoring the blood flow. Many times, a small mesh tube called a stent is also placed in the artery to help it keep open wide.
The procedure itself takes about 1-3 hours and the patient’s usual hospital stay is around 2-3 days.
Fistuloplasty
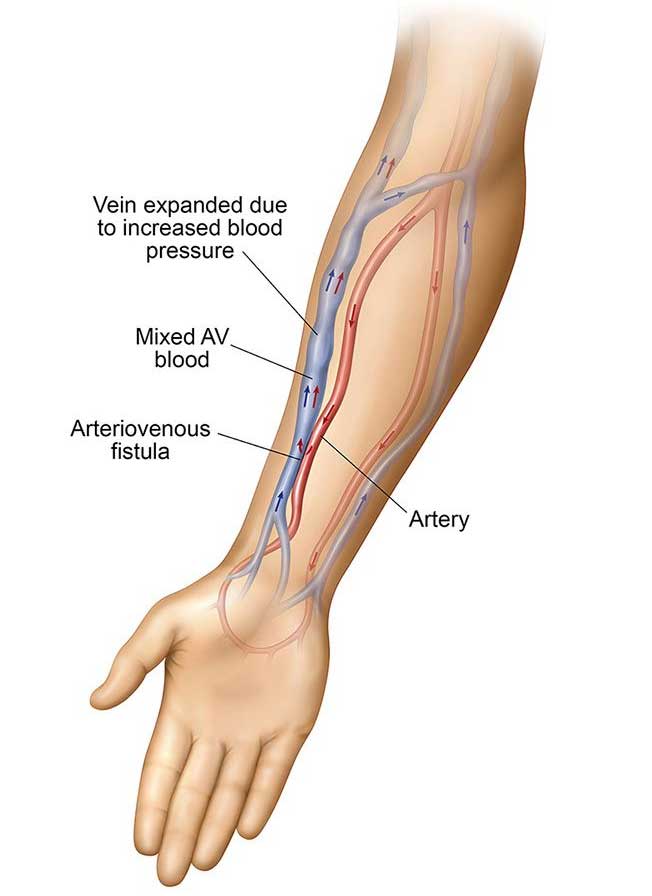
For long-term hemodialysis purposes, Arteriovenous Fistula (AV Fistula) is surgically created by connecting an artery to a vein, usually in the wrist or upper arm. Over the time, the fistula can develop issues like clotting and scarring, which would decrease its functioning and effectiveness of the dialysis which would eventually lead to fistula failure.
Fistuloplasty is a non-surgical procedure performed by an experienced Interventional Radiologist to open the narrowed or blocked blood vessels in the fistula with the use of a special balloon-type device. This is a very safe procedure that carries a very low-risk profile and generally takes about an hour or two, however, the duration differs according the patient’s condition.
This procedure is usually performed under light sedation or local anaesthesia by an expert Interventional Radiologist, who identifies the puncture site by ultrasound and places a small sheath. Under x-ray guidance, an angiogram is performed to see the site of blockage. Once the site is confirmed, the balloon is placed and inflated to open the vessel. After satisfactory flow has been established, the catheter is then pulled out and the skin incision is sealed appropriately.
This procedure is usually performed under light sedation or local anaesthesia by an expert Interventional Radiologist, who identifies the puncture site by ultrasound and places a small sheath. Under x-ray guidance, an angiogram is performed to see the site of blockage. Once the site is confirmed, the balloon is placed and inflated to open the vessel. After satisfactory flow has been established, the catheter is then pulled out and the skin incision is sealed appropriately.