I. Introduction
When monthly bleeding is abnormally heavy or prolonged, it is referred to as menorrhagia. In this condition, a woman’s menstrual cycle lasts for more than seven days, she has to change her sanitary products more than once an hour, or she passes blood clots bigger than a quarter throughout her period. An underlying health issue may be the cause of a woman’s heavy menstrual flow, which might disrupt her everyday life. The severity of heavy bleeding varies from person to person; what one person deems heavy may be considered normal by another.
II. Causes of Heavy Bleeding
Hormonal imbalances
Excessive period bleeding is a symptom of hormonal abnormalities that may interrupt the menstrual cycle, such as an estrogen surplus compared to a progesterone deficit. Hormonal disruptions may play a role in causing heavy periods.
Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that may develop anywhere in the uterus. Muscle and fibrous tissue can contribute to the growth of these tumors. Depending on the size and location of the fibroid, it may cause abnormally heavy menstrual bleeding.
Adenomyosis
When endometrial tissue grows inside the uterus’s musculature, this is called adenomyosis. Uterine enlargement, severe cramping, and heavy bleeding periods are all possible outcomes of this condition. Imaging studies or biopsies are often used to identify adenomyosis, which is more common in women who have given birth to a child.
Uterine polyps
Microcystic growths in the uterine lining are called polyps, and they are almost always harmless. They attach to the uterine wall through a thin filament or base. Uterine fibroids have been linked to abnormal or excessive bleeding, infertility, and repeated miscarriages.
Uterus cancer
Uterine cancer, and more especially endometrial cancer, is a possible cause of heavy menstrual bleeding. It results from unchecked growth of aberrant cells in the uterine lining (endometrium). Symptoms of postmenopausal hemorrhage include severe or prolonged bleeding, pelvic discomfort, and abnormal vaginal discharge.
III. Symptoms of Uterus Problems and Infection
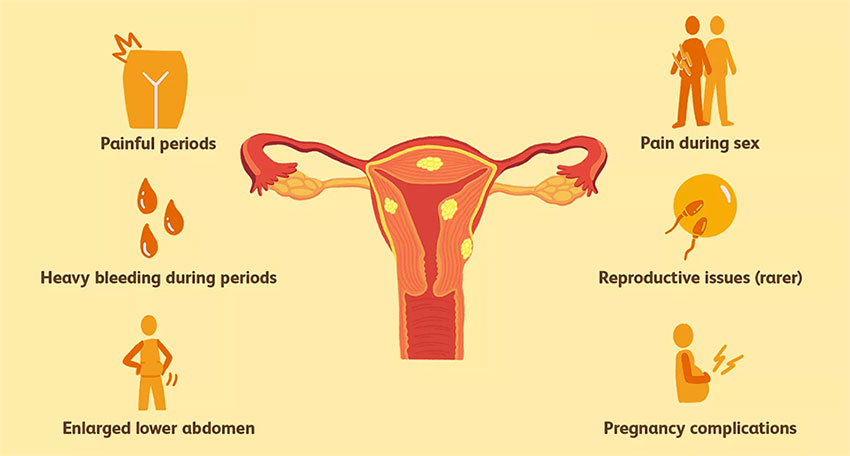
Pain during periods
Infections and abnormalities of the uterus are common sources of pain in period. Spasms may vary from being somewhat uncomfortable to very painful. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), uterine fibroids, endometriosis, and painful periods are all potential causes of menstrual pain.
Abnormal vaginal bleeding
Abnormal vaginal bleeding outside of the menstrual cycle is another symptom of uterus problems and infections, much as heavy monthly bleeding. An abnormal amount of blood leaking from the vagina should raise suspicions of uterine fibroids, hormonal imbalances, or even uterine cancer.
Swelling in the uterus
The Swelling or enlargement of the uterus, also known as bacchedani mai sujan (swelling in the uterus) can occur due to conditions like adenomyosis, or fibroids. It may worsen symptoms such as heavy menstrual flow and pelvic pain and induce a feeling of fullness or pressure in the pelvic area.
IV. Diagnosis of Heavy Bleeding
Medical history
Understanding the root causes of heavy bleeding requires a thorough medical history. Your doctor will want to know details about your menstrual cycles, the frequency and intensity of your bleeding, any other symptoms you’ve had, and any other ailments or drugs you’re taking.
Physical examination
The doctor may assess your general health and the state of your pelvic area by doing a physical examination. An enlarged uterus, fibroids, polyps, or other signs of infection might prompt an examination of the pelvic region.
Imaging-Pelvic ultrasound, TVS, MRI
Diagnostic imaging may help doctors spot structural abnormalities like malignancies in the pelvic region. Pelvic ultrasound is a noninvasive diagnosis that utilizes sound waves to produce images of the pelvic organs. Whereas Transvaginal ultrasound (TVS) involves inserting a specialized ultrasound device into the vagina to get closer and more detailed pictures of the pelvic organs.
V. Treatment of Heavy Bleeding
Medications
Ibuprofen and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help lessen bleeding and pain associated with menstruation. The blood clotting agent tranexamic acid is also used to treat heavy bleeding.
Hormonal therapy
Hormone replacement treatment attempts to do two things at once: normalize menstruation by controlling hormone levels. Common hormonal therapies include gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists and combination oral contraceptives (birth control pills). These drugs lessen heavy periods by balancing out hormone variations that may play a role in them.
Non-surgical procedures
A non-surgical procedure is known to be a medical intervention that does not include any surgical incisions. These methods are applied to resolve bleeding problems without surgery. These procedures are less invasive and can be performed on an outpatient basis. Some common non-surgical procedures for heavy bleeding include:
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) is a minimally invasive surgery used to treat symptomatic uterine fibroids, which may cause heavy bleeding. As an alternative to surgical removal, UFE has been shown to successfully treat heavy menstrual bleeding and other symptoms associated with fibroid tumors.
Microwave Ablation
The most current method used for treating uterine fibroid and other disorders that produce excessive bleeding, Microwave Ablation is a non-invasive method. This procedure allows the tissue to reduce by applying thermal energy.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
The heavy bleeding caused by uterine fibroids may also be treated with Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA), another minimally invasive treatment. It requires less downtime and less pain than surgical alternatives.
Surgical procedures (hysterectomy, myomectomy)
A hysterectomy may be suggested in extreme instances or when other therapies have failed. It’s the only long-term fix for severe bleeding, although it’s usually the last choice.
VI. Resolving Bleeding Problem without Surgery
Lifestyle changes
Keeping a healthy lifestyle may positively affect menstrual health. This calls for regular activity, a diet high in iron and other essential nutrients, and the maintenance of a healthy weight.
Herbal remedies
Herbal treatments are another option, with some evidence suggesting that herbs like ginger, turmeric, and cinnamon may help control menstrual bleeding. Always with your doctor or an experienced herbalist before using any herbal supplements or medications.
VII. Management of Pain during Periods
Pain relief medication
OTC pain relievers like ibuprofen and naproxen can help mitigate menstrual cramping and reduce discomfort.
Heat therapy
The use of a heating device or tepid baths can help soothe the uterine muscles and provide menstrual pain relief.
Relaxation techniques
Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga can help alleviate menstrual discomfort and reduce tension.
VIII. Prevention of Heavy Bleeding
Maintaining a healthy weight
Hormonal abnormalities brought on by being overweight or obese might increase the likelihood of heavy menstrual bleeding. Keeping your weight where it should be might help keep your hormones in check.
Exercising regularly
In addition to improving overall health and reducing the intensity of menstruation symptoms, regular exercise also helps balance hormone levels.
Eating a healthy diet
Keep your diet balanced by eating a mix of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean meats. These foods have been shown to improve general health, including menstruation health.
Managing stress
Hormonal balance and menstruation health are two areas that stress may negatively impact. Activities like exercise, meditation, and therapy help reduce stress.
IX. Conclusion
Finally, if you are experiencing considerable bleeding, medical attention should be sought immediately. The underlying reasons for excessive bleeding must be diagnosed and treated by a medical practitioner, who must be consulted for this purpose. If we want to help women get the treatment they need and improve menstrual health as a whole, we need to get the word out that heavy monthly bleeding is a real problem. Women may improve their health, quality of life, and the likelihood of survival by obtaining medical help as soon as they notice any symptoms. Don’t hesitate to seek help if you’re worried about heavy bleeding or any other period of health issues from your doctor.