I. Introduction
Definition of leg ulcers
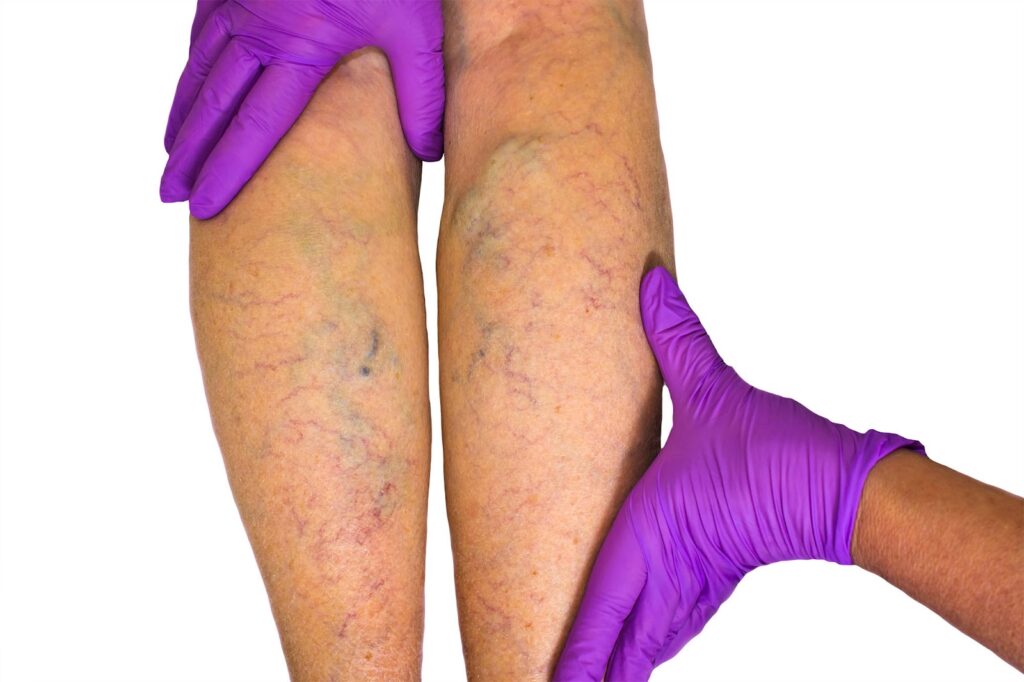
Leg Ulcers are known to be open sores on legs or injuries that transpire on the legs, basically below the knees above the ankle. To be clear, these ulcers are quite painful and might lead to considerable discomfort. Leg Ulcer is notably a medical condition that is caused by numerous underlying factors. In this blog, we will look over what leg ulcer means, what causes them, and when to seek a doctor.
Types of leg ulcers
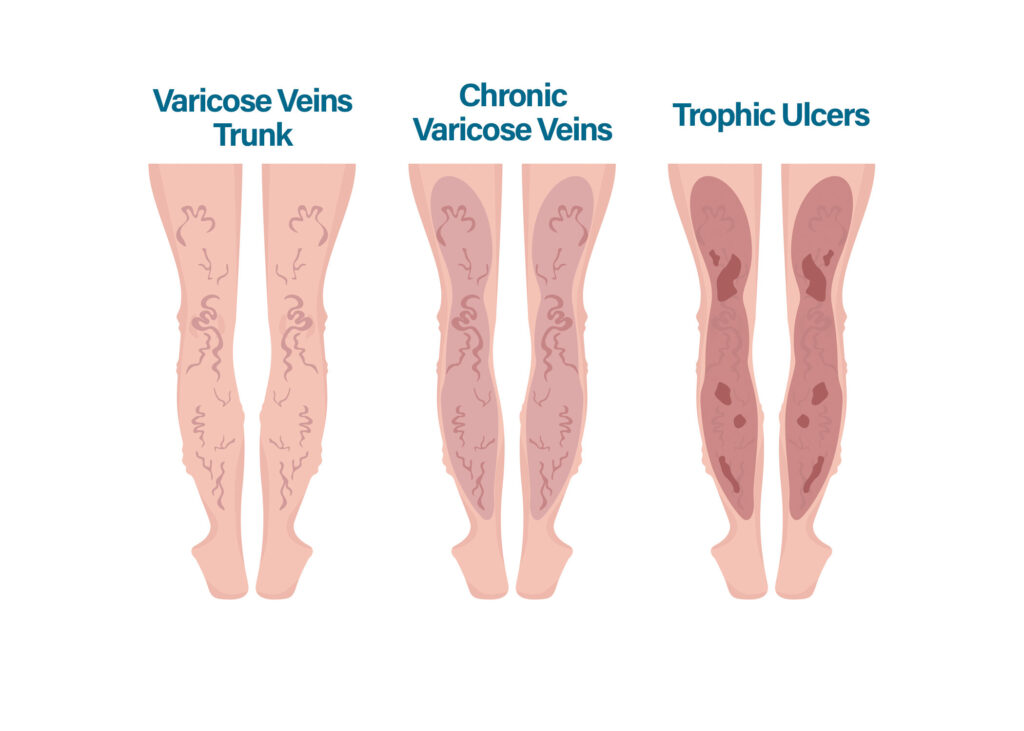
Venous Ulcers: Popularly known as the Stasis Ulcer, Venous Ulcer is the most prevalent kind of ulcer. It may occur because of poor blood circulation within the veins, which may lead up to the building up of pressure in veins and further cause subsequent damage to the underlying tissues.
Arterial Ulcers: This type of leg ulcer occurs due to poor supply of pure blood to the tissue, depriving the region of oxygen and essential nutrients. As a result, the tissues get affected, concluding in the formation of ulcers.
Diabetic Foot Ulcer: Diabetic foot ulcer basically occurs in those individuals who have uncontrolled diabetes. This develops because of neuropathy and poor circulation of blood in the feet, making the wounds in legs difficult to heal.
Neuropathic Ulcer: This type of Ulcer transpires because of nerve damage, resulting in the reduction of an individual’s ability to feel any pain. As a result, the minor injuries on the body go unnoticed and later progress into ulcers.
II. Causes of Leg Ulcers
Venous Insufficiency: Venous ulcers are often linked with chronic venous insufficiency. However, it is a condition wherein the veins fail to pump blood back towards the heart. This led to the pooling of blood in the lower extremities as well as the development of ulcers.
Arterial Insufficiency: Because of the insufficiency of the blood flow into the arteries, commonly caused by atherosclerosis or PAD (Peripheral Artery Disease). Moreover, the decreased supply of blood deprives the tissues of essential nutrients as well as oxygen that cause the formation of ulcers.
Trauma or Injury: Leg ulcers can be caused by the injuries like burns or cuts that break into the skin’s integrity while compromising the healing process.
Infections: If left untreated, viral, fungal, or bacterial infections can lead to ulcers, especially in people that have compromised immune systems.
Neurogenic Factors: Due to reduced pain perception and an inability to identify injuries, neuropathic ulcers may form as a result of nerve damage, such as that caused by diabetic neuropathy or other neuropathic diseases.
III. Symptoms of Leg Ulcers
Pain and Discomfort: In case you are having a leg ulcer, you might be having pain that can vary from mild to severe. The level of pain and discomfort depends upon the underlying cause as well as the stage of the ulcer.
Swelling: The infected region might turn into swelling because of the accumulation of fluid. Furthermore, such swelling can lead to discomfort and affect the healing process.
Odor: Some leg ulcers emit a foul odor, particularly when they are infected. Bacterial growth and tissue breakdown in the ulcer can lead to an unpleasant smell.
IV. Diagnosis of Leg Ulcers
Medical history: First, the doctor will ask you a lot of questions about your health and wellness, such as whether you’ve ever been injured or if you have any chronic problems in your family. The risk factors for leg ulcers can only be determined after a thorough understanding of the patient’s general health.
Physical examination: After a thorough history and physical examination of the patient, the size, location, and appearance of the ulcer may be determined. A doctor will also examine the patient for signs of infection, tissue damage, and circulation problems.
Imaging tests: Imaging studies may be required in order to assess the severity of the ulcer and the blood supply to the affected region. Doppler ultrasonography is widely used as a noninvasive method of assessing blood flow.
V. Treatment of Leg Ulcers
Traditional treatment options: Treatment options for venous leg ulcers include compression therapy, whereby the patient wears or applies a compression garment or dressing. These garments are designed to provide pressure to the legs, which improves circulation, minimizes swelling, and accelerates the healing of wounds. Hydrocolloids, foams, alginates, and gauze are some of the wound dressings utilized for leg ulcers. These dressings keep the wound moist to reduce infection and speed recovery.
Varicose ulcer treatment: Leg ulcers caused by venous insufficiency are known as varicose ulcers. Treatment for varicose ulcers should focus on fixing the underlying vein problem. Some potential treatments include compression bandages or stockings, as was previously mentioned, to help improve blood flow and lessen swelling in the legs. Endovenous laser ablation is a non-surgical method of closing up diseased veins and rerouting blood flow to more functional veins. In sclerotherapy, a sclerosing substance is injected into the veins that are causing problems, causing them to shut and rerouting blood flow to healthier veins. The medical field has made significant progress in treating varicose veins with the introduction of Venaseal or glue therapy.
PRP therapy: PRP treatment makes use of a highly concentrated version of the patient’s blood that’s rich in platelets and growth factors to speed up the healing process after an injury. Platelet-rich plasma is extracted from a blood sample and injected into or applied topically to the leg ulcer. PRP treatment has been shown to increase tissue repair and regeneration and is a new treatment for leg ulcers.
VI. Prevention of Leg Ulcers
Preventing leg ulcers is crucial for keeping one’s health and well-being in check. The following are some necessary precautions:
Maintaining good hygiene: In order to avoid infections and tissue breakdown, it is crucial to maintain the legs clean and dry at all times. Maintain a routine of washing with saline to remove dead and dry skin, along with keeping good hydration with medically recommended moisturizer.
Managing chronic conditions: The prevention of leg ulcers in those with preexisting diseases such as diabetes or eczema necessitates careful treatment of these disorders. Follow your dermatologist’s advice and make sure your blood sugar is stable if you have diabetes and eczema.
Exercise and healthy lifestyle habits: Healthy eating and regular exercise are two of the best ways to boost your circulation and overall vascular health. In addition, a healthy lifestyle, including balanced food and not smoking, helps maintain a healthy epidermis and cardiovascular system.
VII. When to Seek Medical Attention
Leg ulcer symptoms include but are not limited to the following and need prompt medical intervention. Infection or poor healing may be the cause of ongoing pain around an open incision or ulcer, therefore it’s important to take such discomfort seriously from the outset. Moreover, if you see significant edema in your legs, especially around the ulcer site, it may suggest compromised circulation or an underlying problem that needs rapid treatment by a healthcare specialist. Another red flag that calls for medical treatment is the existence of a foul odor or an unusual discharge from the ulcer. In addition, you should seek medical attention if you see any signs of infection or inflammation, such as increased heat, redness, or pain in the skin around the ulcer.
VIII. Conclusion
Leg ulcers are more than simply an annoyance; they may have a major effect on a person’s standard of living. Developing leg ulcers is avoidable if you practice good cleanliness, take care of any underlying chronic diseases you may have, and stick to a generally healthy diet and exercise routine. However, if any worrying symptoms appear, it is crucial to visit a doctor right once. Complications may be avoided and recovery can go more smoothly if the problem is diagnosed and treated early. Keep in mind that avoiding leg ulcers and keeping your legs in good condition requires you to take preventative measures.