What is Peripheral Artery Disease?
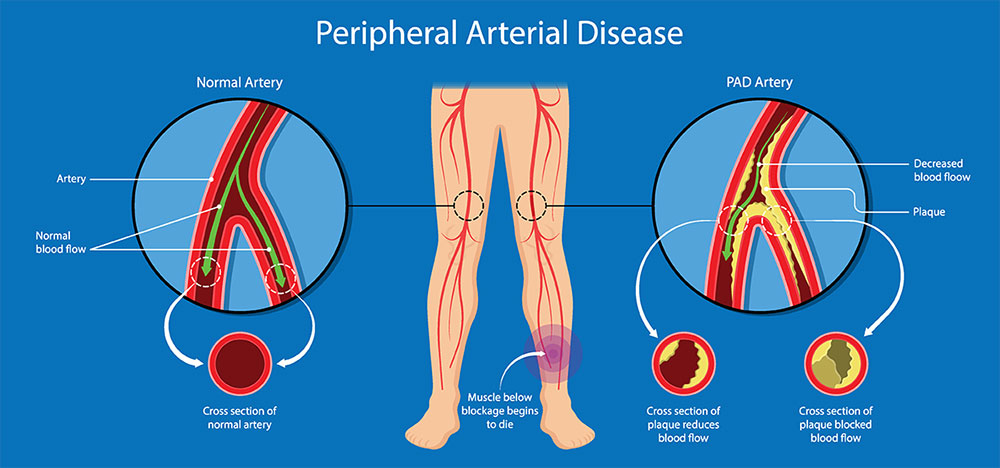
Peripheral artery disease also called peripheral vascular disease is a common circulatory problem in which tubes called arteries, that supplies blood to limbs gets narrowed.
Usually, it can affect any organ but most commonly involves lower limbs. Arteries that supply blood to the legs can become narrow over time due to fatty plaque buildup that blocks or restricts blood flow, making it painful to walk.
Peripheral artery disease (PAD), extremities don’t receive enough blood to meet the demand and muscle get fatigued due to low oxygen supply and develops pain while walking, known as claudication.
How Flowcare Can Help You with Peripheral Artery Disease
Management of PAD needs multidisciplinary approach needs interventional Radiologist, vascular surgeon, endocrinologist, and dietitian. Flowcare has expertise and resources for the diagnosis, treatment, and management of the peripheral arterial disease. With our unique depth of knowledge, diagnostic expertise and state-of-the-art imaging, we customize treatment plans for each individual PAD patient to ensure the best possible outcome.
Flowcare is providing world-class treatment with a focus on optimal patient care. We offer several minimally invasive, outpatient procedures for the patients who have been diagnosed with the peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
In addition, Flowcare Intervention clinic provides a full range of medical capabilities and service excellence to every patient. We ensure an easy scheduling process with a team of medical experts who provides excellent outcomes and a quick recovery.
Symptoms:
Peripheral artery disease signs and symptoms include:
- Severe pain in thigh or calf during walking or climbing stairs (claudication)
- Leg numbness, weakness or calf atrophy
- Coldness in leg or foot, especially when compared with the other side
- Change in the color of skin or hair loss over at the affected area
- Shiny skin on your legs
- No pulse or a weak pulse in your legs or feet
- Sores on your toes, feet or legs that won’t heal
- Erectile dysfunction in men
- Pain while resting in advance stage
When to see a doctor
If you have symptoms in the legs e.g. like pain, numbness or swelling than consult your doctor.
Even if you don’t have symptoms of peripheral artery disease, you may need to be screened if you are:
- Age above to 65
- Age above to 50 with a history of diabetes or smoking.
- Under age 50, with a history of diabetes and other risk factors like obesity, high blood pressure, etc.
Diagnosis
Some of the tests your doctor may rely on to diagnose peripheral artery disease are:
Physical exam.
Your doctor may find signs of PAD during a physical examination, such as a weak or absent pulse below a narrowed area of your artery, whooshing sounds (bruits) over your arteries that can be heard with a stethoscope, evidence of poor wound healing in the area where your blood flow is restricted, and decreased blood pressure in your affected limb.
Ankle-brachial index (ABI).
This is a common test used to diagnose PAD. It compares the blood pressure in your ankle with the blood pressure in your arm.
Color Doppler Ultrasound
It is an imaging technique, such as Doppler ultrasound, can help your doctor evaluate blood flow through your blood vessels and identify blocked or narrowed arteries.
Angiography
There is two way
1. Imaging techniques like called magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) or computerized tomography angiography (CTA).
2. Conventional Angiography or Digital subtraction angiography (DSA)
Blood tests:
A sample of your blood is taken to measure your cholesterol and triglycerides and to check for diabetes.
Causes
Development of atherosclerosis
Peripheral artery disease is often due to the deposition of fat (Plaques) in walls of arteries, a process is known as atherosclerosis and results in the reduced blood flow.
Most commonly it affects heart and brain known as heart attack or stroke but when it occurs in the arteries supplying blood to your limbs, it causes peripheral artery disease.
Risk factors
Factors that increase your risk of developing peripheral artery disease include:
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity (a body mass index over 30)
- High blood pressure
- Having High cholesterol
- Increasing age, especially after reaching 50 years of age
- A family history of peripheral artery disease, heart disease or stroke
- High levels of homocysteine, a protein component that helps build and maintain tissue
- People who smoke or have diabetes have the greatest risk of developing peripheral artery disease due to reduced blood flow.
Complications:
If your peripheral artery disease is due to the buildup of plaques in your blood vessels (atherosclerosis), you’re also at risk of developing.
1.Critical limb ischemia. This condition begins as open sores that don’t heal, an injury, or an infection of your feet or legs. Critical limb ischemia occurs when such injuries or infections progress and cause tissue death (gangrene), sometimes requiring amputation of the affected limb.
2.Acute limb ischemia. Due to sudden complete blockage of blood supply, there is excessive pain and blackening of skin(Gangrene) which requires immediate treatment otherwise limb salvage.
3.Stroke and heart attack. Atherosclerosis that causes the signs and symptoms of peripheral artery disease isn’t limited to your legs. Fat deposits also build up in arteries supplying blood to your heart and brain.
Treatments for Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Treatment for peripheral artery disease has two major goals:
- To increase the blood supply of the affected region so that you can resume your physical activities without any pain.
- Stop the progression of atherosclerosis throughout your body to reduce your risk of heart attack and stroke
Your doctor prescribes the medicines to prevent progression of the disease to increase the blood supply by vasodilators, blood thinners, antihypertensive and pain killers.
Angioplasty and surgery
In some cases, angioplasty or surgery may be necessary to treat peripheral artery disease that’s causing claudication. In this procedure, a small hollow tube (catheter) is threaded through a blood vessel to the affected artery. There, a small balloon on the tip of the catheter is inflated to reopen the artery and flatten the blockage into the artery wall, while at the same time stretching the artery open to increase blood flow.
Supervised exercise program
In addition to medications or surgery, your doctor likely will prescribe a supervised exercise training program to increase the distance you can walk pain-free. Regular exercise improves symptoms of PAD in a number of ways, by helping your body use oxygen more efficiently.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Many people can manage the symptoms of peripheral artery disease and stop the progression of the disease through lifestyle changes, especially quitting smoking.
Careful foot care
In addition to the above suggestions, take good care of your feet. People with peripheral artery disease, especially those who also have diabetes, are at risk of poor healing of sores and injuries on the lower legs and feet.
Prevention:
The best way to prevent claudication is to maintain a healthy lifestyle. That means:
- Quit smoking.
- If you have diabetes, keep your blood sugar in good control.
- Exercise regularly: Aim for 30 to 45 minutes several times a week.
- Lower your cholesterol and blood pressure levels.
- Eat foods that are low in saturated fat.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
Conclusion
Hence, If you are experiencing symptoms of PAD, particularly chronic wounds or sores on your feet, comes at Flowcare Intervention & Pain Clinic immediately. The sooner you will diagnose with PAD and start the treatment, it will lower your risk of the disease progressing. If you left untreated for a long time then amputation will be the only option.



