What Is Varicocele and How Can It Impact Male Fertility?
Varicocele affects more men than you might realize, yet many are unaware they have the condition.
Studies show that around 15% to 20% of adult men develop a varicocele, a condition that can impact testicular health, male fertility, and overall confidence.
In fact, research indicates that up to 40% of men undergoing evaluation for infertility are found to have a varicocele.
This condition is especially common in men of reproductive age and has significant clinical implications, as it can lead to abnormal semen analysis, reduced sperm motility, poor sperm morphology, and low sperm count.
Understanding varicocele and taking early preventive steps is crucial. Read on to learn more about its causes, signs and symptoms, treatment options, and ways to manage it effectively.
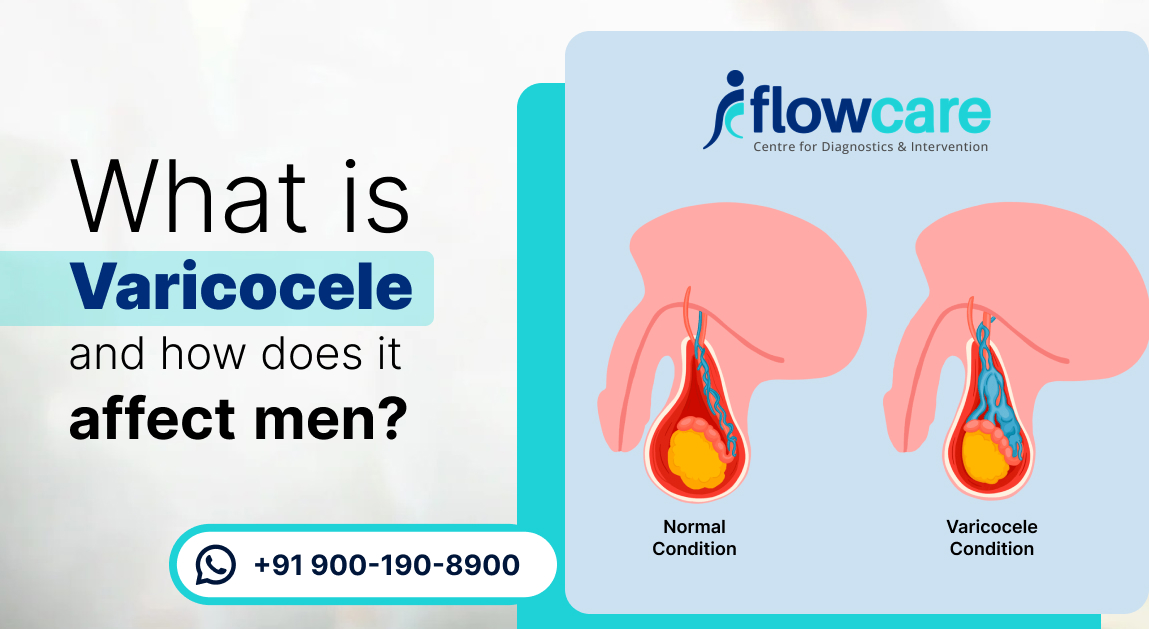
What is Varicocele?
Varicocele is a common condition characterized by the abnormal dilation and enlargement of the veins within the scrotum, specifically the pampiniform plexus, which drains blood from each testicle.
In varicocele, the veins become enlarged, similar to varicose veins in the legs.
This condition is also known as “a bag of worms”. Commonly seen in the male population.
A bag of worms has a 17%-41% contribution rate in progressive male infertility. (2)
The condition is often classified into small, medium, and large. Many times, varicocele remains asymptomatic, but in a few cases, varicose-like veins can cause:
- Discomfort
- Impaired fertility
- Testicular atrophy
What Causes Varicocele in Men? Key Reasons & Risk Factors Explained
Varicocele in men is caused by malfunctioning valves inside the veins that should send blood from the testicles to the heart.
They are designed to ensure that blood circulation moves upward against gravity. If something weakens the valves, blood will pool and go back the other way, especially while standing.
This results in a big, twisted bunch of veins that may feel like you’re holding a bag of worms.
Notably, 78%-93 % of cases of varicocele are located on the left side. (3)
What Causes Valve Dysfunction? Key Factors You Should Know
While the exact cause is not always clear, several factors can increase the risk:
- Age: According to the study, this condition is often seen in patients of reproductive age. As men age, vein valves and walls weaken naturally, increasing valve failure risk.
- Heavy Weight Lifting: Straining during physical activity can increase abdominal pressure, which in turn can disrupt the flow in the testicular veins.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Sitting for long hours can weaken the blood flow, especially in the groin & pelvic area.
- Kidney Tumors: Though this is not common, tumors in the kidney can block blood drainage from the testicles by squeezing nearby veins on the left side.
- Blockage of the Spermatic Cord: Any change in the anatomy of this region can affect the vein’s function and encourage blood to pool.
- Hormonal Imbalances: A lack of testosterone in the blood may disrupt the tone of blood vessels and lead to trouble with blood flow.
- Genetics: Varicose veins or varicocele are more common in people with a similar condition in their family.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle: such as smoking, drinking, or occupational exposure to certain elements. (4)
Varicocele Symptoms: Signs Every Man Should Watch For
Most varicoceles are asymptomatic and may go unnoticed unless complications arise or are found during a routine physical exam. When symptoms occur, they may include:
- Dull, aching pain or discomfort in the scrotum, often worsening when standing or after physical activity.
- A visible or palpable mass in the scrotum, sometimes described as feeling like a “bag of worms”.
- Swelling or a lump in the scrotum, usually on the left side.
- Decreased testicle size (testicular atrophy) on the affected side.
- Infertility or problems with sperm quality and production.
- Heaviness in the testicle, especially later in the day or after exertion.
Varicocele Grading Explained: Know the Stages & Severity
Varicocele grades help doctors assess severity and decide whether surgery or monitoring is needed.
Sarteschi Classification for Color Doppler Ultrasound Diagnosis of Varicocele
| Grade | Description |
| Grade 1 | Venous reflux at the emergence of the scrotal vein only during the Valsalva maneuver; hypertrophy of the venous wall without stasis |
| Grade 2 | Supratentorial reflux only during the Valsalva maneuver; venous stasis without varicosities |
| Grade 3 | Peritesticular reflux during the Valsalva maneuver; overt varicocele with early-stage varices of the cremasteric vein |
| Grade 4 | Spontaneous basal reflux that increases during the Valsalva maneuver; possible testicular hypotrophy, overt varicocele, varicosities in the pampiniform plexus |
| Grade 5 | Spontaneous basal reflux that does not increase during the Valsalva maneuver; testicular hypotrophy, overt varicocele, varicosities in the pampiniform plexus |
→ 1. Grades 1–3 require the Valsalva maneuver to trigger reflux.
→ 2. Grades 4–5 show spontaneous reflux even at rest.
→ 3. Grade 5 suggests a more severe, chronic condition where reflux is constant and testicular damage is likely.
Varicocele Grade 4 Symptoms: What Men Need to Know
Varicocele grade 4 is the most severe condition, characterized by noticeable swelling, pain, and a decreased size of the affected testicle.
The symptoms include:
- Pain: A dull, aching pain or discomfort in the scrotum that worsens with standing or physical activity, and may improve when lying down.
- Swelling: A noticeable swelling or lump in the scrotum, often described as feeling like a “bag of worms”.
- Testicular Atrophy: In some cases, the affected testicle may shrink in size due to reduced blood flow and pressure.
- Infertility: Varicoceles can affect sperm production and quality, potentially leading to difficulty conceiving.
- Other: Some individuals may also experience a feeling of heaviness or dragging in the scrotum, or notice dilated veins in the scrotum that can be felt or seen.
How Is This Condition Diagnosed? Key Tests & Methods Explained
The diagnosis can be made through physical examination techniques like the Valsalva maneuver and imaging tests like color Doppler ultrasound.
What is the Treatment for Varicocele?
With mild cases of varicocele (grades 1 and 2), making changes to your lifestyle and taking extra care is generally enough to control it.
However, for symptomatic Grade 3 or 4 varicoceles, definitive medical or surgical treatment is typically recommended.
When left untreated, testicular atrophy and infertility can occur in men because of higher-grade varicoceles.
H3: What are the Varicocele Surgery Requirements?
Surgery might be recommended in the following conditions:
- Delayed development of the testicles
- Lower or decreased sperm count
- Chronic pain not managed by pain medication
The surgery is done to redirect the blood flow into healthy veins. The following are the two approaches followed during a surgical process:
- Microscopic varicocelectomy: The procedure usually takes 1-2 hours, where the surgeon makes a small incision in the groin (the abdomen and the upper thigh area). Through a microscope, the small damaged veins are tied up.
- Laparoscopic varicocelectomy: The procedure uses a video camera and a tube that passes through small incisions in the upper groin area. The procedure takes 60-90 minutes.
Source: mayoclinic(5)
Varicocele Treatment Without Surgery: Safe Non-Surgical Options
Patients can also opt for non-surgical options for the treatment of varicocele. While surgical treatments may lead to complications such as infections, bleeding, etc
Non-surgical options, such as varicocele embolization, are safer than surgical ones.
Varicocele Embolization Procedure: Step-by-Step Guide for Patients
The percutaneous embolization procedure involves blocking the damaged vein in the scrotum using coils or glue, which redirects the blood into healthier veins.
- A radiologist makes a small incision in the groin area, and a catheter is then used to visualize the scrotal veins with contrast dye.
- The swollen and incompetent veins are identified and blocked using coils, glue or other materials.
- This redirects blood flow to healthier veins, effectively shutting off the unhealthy ones without surgery.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
- Avoid heavy lifting and engage in regular exercise
- Antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium might improve sperm health in varicocele patients, and should be discussed with a qualified doctor
Conclusion
Varicocele is a common condition in men, yet many remain unaware they have it.
For most, lifestyle changes and simple precautions provide relief. However, varicoceles that lead to fertility challenges or persistent discomfort require evaluation by a doctor or specialist.
Early detection of testicular issues can help prevent complications like testicular shrinkage and difficulties with conceiving.
Treatment options may include surgical intervention to repair the veins or minimally invasive procedures such as embolization, both of which can effectively address varicoceles.
In addition, adopting a healthy lifestyle and taking specific supplements may support reproductive health.
If you experience symptoms or are concerned about your fertility, consulting a healthcare professional is the best step to manage the condition effectively.
FAQs
What is varicocele?
A varicocele may cause problems with the testicles’ temperature. When stress oxidizes the body’s cells, toxins can start to accumulate.
How does varicocele affect men?
Varicocele affects men in the following way:
- Low testicular function: As boys enter puberty, a varicocele might hinder the testicles’ development, hormone secretion, and other functions. A varicocele in men may gradually reduce due to a loss of tissue.
- Infertility
What is the root cause of varicocele?
Varicoceles are thought to develop from venous blood flow in the internal spermatic vein that causes venous engorgement, which is clinically detectable on scrotal examination.






