Living with Trigeminal Neuralgia: Coping Mechanisms and Support Resources
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a debilitating condition characterized by severe facial pain, often described as sharp, stabbing, or electric shock-like sensations. This chronic pain disorder affects the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for transmitting sensory information from the face to the brain. The intensity of pain episodes can be excruciating, significantly impacting the quality of life. However, with appropriate coping mechanisms and support resources, it is possible to manage the challenges associated with living with trigeminal neuralgia.
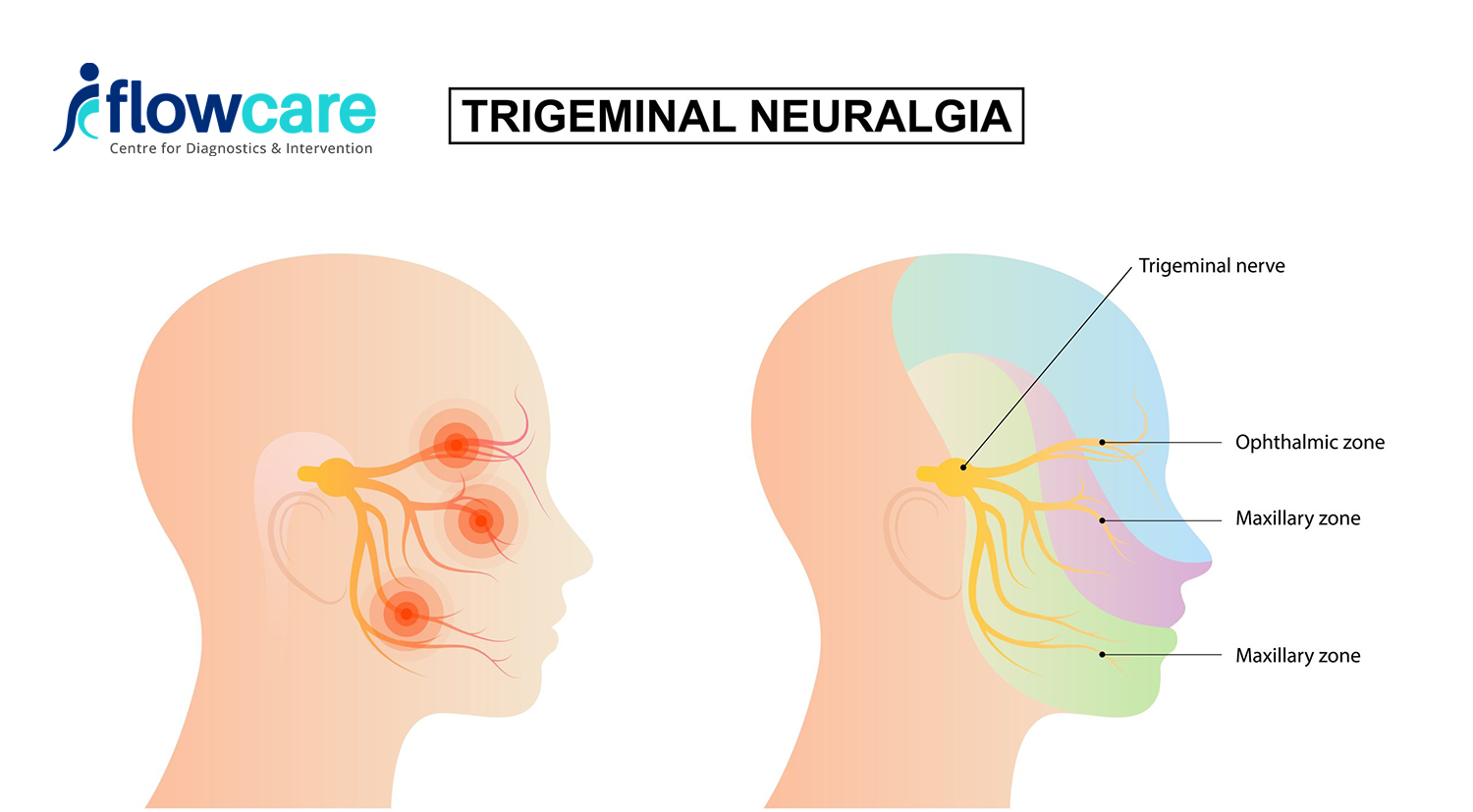
What is Trigeminal Neuralgia ?
The trigeminal nerve, also known as the fifth cranial nerve, is one of the largest nerves in the head and is responsible for providing sensation to the face, including the forehead, cheeks, jaw, and teeth. Trigeminal neuralgia occurs when this nerve is compressed or irritated, leading to episodes of intense facial pain. These episodes can be triggered by seemingly innocuous stimuli such as touching the face, chewing, or even a gentle breeze.
Treatment Options for Trigeminal Neuralgia:
Managing trigeminal neuralgia often requires a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals from various specialties, including neurology, pain management, and interventional radiology. One of the advanced treatment modalities gaining prominence in recent years is radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for trigeminal neuralgia. RFA involves the use of heat generated by radiofrequency waves to target and selectively destroy the nerve fibers responsible for transmitting pain signals. This minimally invasive procedure offers significant relief for many patients suffering from trigeminal neuralgia, reducing the frequency and severity of pain episodes.

Coping Mechanisms for Trigeminal Neuralgia:
Living with trigeminal neuralgia can be challenging, but there are several coping mechanisms that individuals can adopt to improve their quality of life Certainly! Let’s delve into each coping mechanism for living with trigeminal neuralgia in more detail:
- Medication Management:
Medications play a vital role in managing trigeminal neuralgia symptoms. Commonly prescribed medications include anticonvulsants like carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, and gabapentin, which work by stabilizing nerve cell membranes to reduce pain signals. Tricyclic antidepressants such as amitriptyline and nortriptyline may also be prescribed to help alleviate nerve pain. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to find the most effective medication regimen while monitoring for potential side effects.
- Mind-Body Techniques:
Mind-body techniques focus on the connection between mental and physical health, offering holistic approaches to managing pain and reducing stress. Practices such as meditation, mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, and guided imagery can help individuals relax their muscles, calm their minds, and redirect their focus away from pain sensations. These techniques can be integrated into daily routines or used during pain flare-ups to promote relaxation and well-being.
- Heat and Cold Therapy:
Heat and cold therapy are non-invasive methods used to alleviate trigeminal neuralgia symptoms. Applying heat packs or warm compresses to the affected areas can help increase blood flow, relax tense muscles, and provide temporary pain relief. Conversely, cold packs or ice packs can help numb the area, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain. Individuals may experiment with both heat and cold therapy to determine which option offers the most relief for their specific symptoms.
- Dietary Modifications:
Certain foods and beverages have been known to trigger trigeminal neuralgia pain episodes in some individuals. Common triggers include caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, citrus fruits, and foods high in sugar or artificial additives. By identifying and avoiding these triggers, individuals can minimize discomfort and reduce the frequency of pain flare-ups. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can also support overall health and well-being.
- Support Groups:
Connecting with others who understand the challenges of living with trigeminal neuralgia can provide invaluable emotional support and practical advice. Support groups, whether in-person or online, offer a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, exchange coping strategies, and offer encouragement to one another. By fostering a sense of community and belonging, support groups help individuals feel less isolated and better equipped to navigate their journey with trigeminal neuralgia.
- Alternative Therapies:
Complementary and alternative therapies offer additional options for managing trigeminal neuralgia symptoms. Acupuncture, for example, involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow and promote pain relief. Chiropractic care focuses on spinal adjustments and manipulations to improve nerve function and alleviate pain. Biofeedback utilizes electronic sensors to monitor physiological responses and teaches individuals how to control bodily processes such as muscle tension and heart rate, potentially reducing pain perception.
Overall, adopting a multidimensional approach that incorporates medication management, mind-body techniques, heat and cold therapy, dietary modifications, support group participation, and alternative therapies can empower individuals to effectively manage their trigeminal neuralgia symptoms and improve their quality of life. It’s essential to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses individual needs and preferences.

Support Resources for Individuals with Trigeminal Neuralgia:
In addition to implementing coping mechanisms, accessing support resources can be instrumental in managing trigeminal neuralgia:
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Association (TNA): TNA is a nonprofit organization dedicated to providing support, education, and advocacy for individuals affected by trigeminal neuralgia.
- Online Communities: Websites and social media groups focused on trigeminal neuralgia provide a platform for individuals to connect, share experiences, and access information about treatment options.
- Patient Education Materials: Healthcare providers and organizations often offer educational materials and resources to help individuals better understand their condition and navigate treatment decisions.
- Pain Management Clinics: Specialized pain management clinics may offer comprehensive care for individuals with trigeminal neuralgia, including access to interventional procedures and psychological support services.
- Interventional Radiologists: These specialists play a crucial role in performing radiofrequency ablation procedures for trigeminal neuralgia, offering expertise in minimally invasive techniques to alleviate pain.
Final Words:
Living with trigeminal neuralgia presents unique challenges, but with the right combination of treatment modalities, coping mechanisms, and support resources, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Radiofrequency ablation, along with other interventions, holds promise in providing long-lasting relief for those affected by this debilitating condition. By proactively addressing pain management strategies and seeking support from healthcare professionals and peer networks, individuals with trigeminal neuralgia can navigate their journey with resilience and hope.